The Ultimate Guide: Difference Between Data Science, Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning

Have you ever felt confused about the terms Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning?
You’re not alone. Many people use these words interchangeably, but they are not the same.
They are related, but each has a unique role.
In this guide, we’ll break down these concepts in simple language.
We’ll explore what each field is, how they relate to one another, and their real-world applications.
By the end, you’ll clearly understand these three exciting fields. This will help you decide which path is right for you.
Unlock your future in tech — start mastering Data Analytics, AI, and ML today.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Basics
To understand the differences, let’s first define each term. Think of them as different tools in a toolbox. Each tool has a specific job.
What is Data Science?
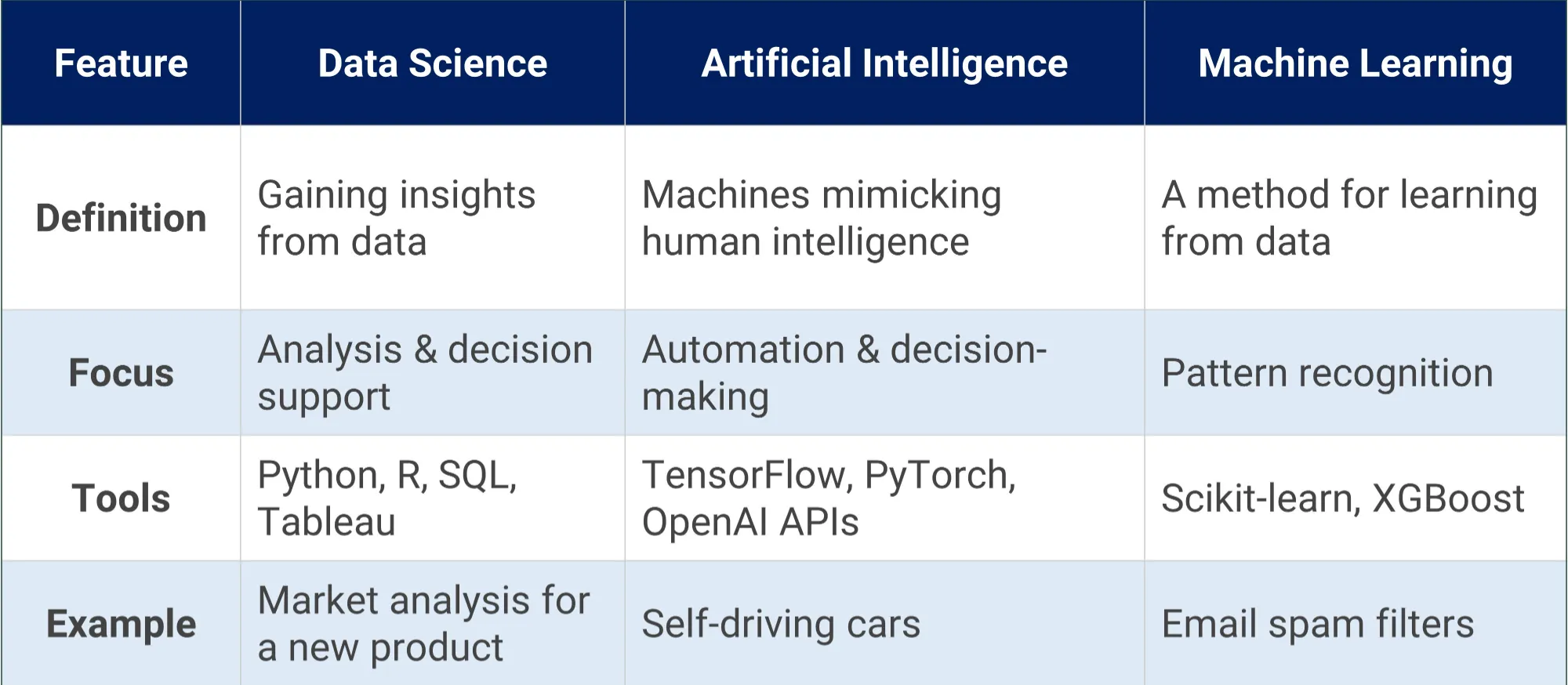
Data Science is all about getting insights from data. A data scientist’s main job is to find patterns and make predictions from a lot of information. They use a mix of skills. These include statistics, programming, and knowledge of a specific business area.
The process usually starts with collecting data. Then, they clean and organize it. After that, they analyze the data and create visualizations like charts and graphs. Finally, they use this information to help a company make smart decisions. Tools like Python, R, SQL, Tableau, and Power BI are very common in this field.
For example, a data scientist might analyze customer data for an e-commerce company. They would predict future sales. This helps the company prepare for busy seasons.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the biggest and broadest field. Its main goal is to create machines that can think and behave like humans. AI systems can learn, reason, and solve problems on their own.
AI is not just about robots. It includes many different areas. Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision are some of its key branches. Developers often use tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and OpenAI APIs to build AI systems.
A great example of AI is the language translation you see online. A system translates text from English to Hindi automatically. This system mimics a human translator’s ability to understand language.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning (ML) is a special part of AI. Its focus is on making computers learn from data without being directly programmed. Instead of writing rules for every possible situation, you feed a computer a lot of data. The machine then finds patterns and makes its own rules.
There are different types of Machine Learning. Supervised learning uses labeled data to make predictions. Unsupervised learning finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data. Reinforcement learning teaches a system through trial and error. Some popular algorithms are Decision Trees, Neural Networks, and Random Forest. Tools like Scikit-learn, Keras, and XGBoost are widely used.
A classic example is a credit card fraud detection system. The system learns from past transaction data. It identifies unusual patterns to flag potentially fraudulent activity.
Your dream career is just one skill away — take the first step now.
Relationship Between Data Science, AI & ML
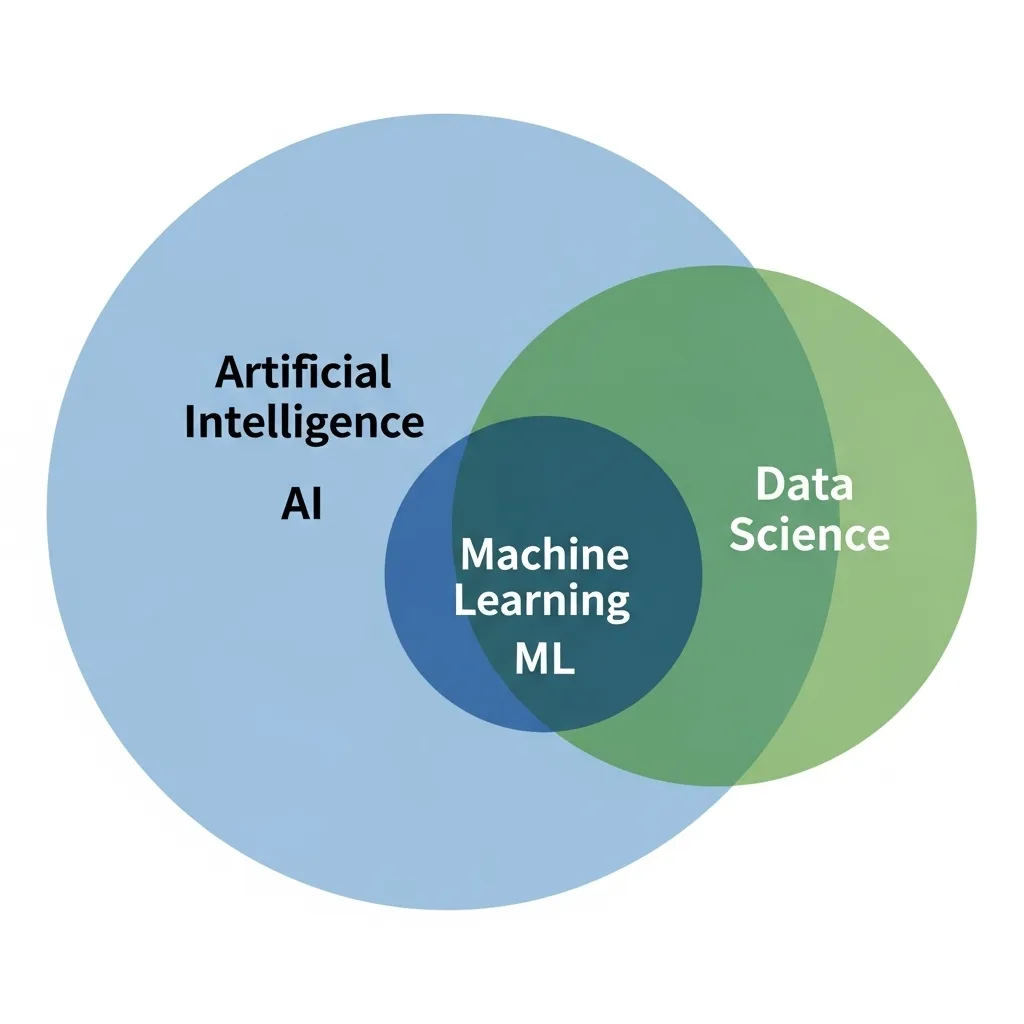
This is where things can get confusing. The best way to think about it is with nested circles .
AI is the largest circle. It’s the overall concept of creating smart machines. ML is a smaller circle inside AI. It’s a specific method for achieving AI. In other words, you use Machine Learning to build a powerful AI system. Data Science is a circle that overlaps with both. A data scientist uses many tools, and Machine Learning is one of them. For instance, a data scientist might use an ML algorithm to predict customer churn. So, while Data Science is a separate field, it heavily uses ML.
Think of it like this: A Data Scientist is a detective who uses clues (data) to solve a case. Sometimes, they use a special magnifying glass (ML) to find complex clues. The goal of the detective is to find insights. The magnifying glass is just one of their tools.
Key Differences at a Glance
Real-World Applications
These fields are changing the world around us. Let’s look at some examples you might already be familiar with.
Applications of Data Science
Business Analytics: A retail company analyzes sales data. It finds out which products are most popular in different regions. This helps them manage their inventory better.
Healthcare Predictions: Doctors use patient data to predict the risk of diseases. This helps in early diagnosis.
Sports Performance: Teams analyze player statistics. They predict player performance and strategize for future games.
Applications of AI
Virtual Assistants: Your smart speaker (like Alexa or Google Assistant) uses AI to understand your voice commands and respond.
Facial Recognition: The system that unlocks your phone using your face is a result of AI.
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars are the best example of AI. They use various sensors and AI algorithms to navigate.
Applications of ML
Product Recommendations: When Netflix suggests a movie you might like, it’s using ML. The system learns from your viewing history and what other people with similar tastes watch.
Fraud Detection: Your bank uses ML algorithms to check for unusual transactions. If it sees a large purchase in a new city, it might flag it as potentially fraudulent.
Predictive Maintenance: Factories use sensors on machines. ML models analyze the sensor data to predict when a machine might break down. This helps in performing maintenance before a failure occurs.
Don’t just read about the future, be the one who builds it.
Career Opportunities
These fields offer excellent career paths with high growth potential.
Jobs in Data Science
A Data Scientist uses data to answer complex business questions. A Data Analyst focuses on collecting, cleaning, and interpreting data. A BI Analyst creates reports and dashboards for business insights.
Jobs in AI
An AI Engineer builds and manages AI systems. A Robotics Engineer designs and programs robots. An NLP Specialist works on systems that process human language.
Jobs in ML
An ML Engineer builds and deploys machine learning models. A Computer Vision Engineer works on systems that can “see” and interpret images. A Research Scientist focuses on developing new ML algorithms.
Which Should You Learn First?
If you are a beginner, starting with Data Science is a great choice. It gives you a strong foundation in statistics, programming, and data handling. Once you are comfortable with data, you can easily transition to Machine Learning. You’ll use your data skills to build powerful predictive models. AI is a vast field. Learning about ML and Data Science first will give you the right skills to explore AI’s broader applications.
There are many resources available online to get started. For a deeper dive into these topics, consider exploring tutorials and courses on platforms like Kaggle. You can find excellent resources to get hands-on experience and build your portfolio [Link: https://www.kaggle.com].
Conclusion
We’ve learned that Data Science, AI, and ML are related but distinct. AI is the big goal of creating intelligent machines. ML is a powerful tool to achieve that goal. Data Science is a field that uses many tools, including ML, to extract valuable insights from data. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right path and find your place in the future of technology.
FAQs
Is Data Science a part of AI?
Not exactly. Data Science and AI are two different fields, but they have a lot of overlap. A data scientist may use AI and ML tools to get insights, but a data scientist’s job is not always focused on building AI systems.
Can AI exist without ML?
Yes, it can. AI is a broad field. There are old forms of AI that use fixed rules and logic to solve problems. However, today’s most advanced and popular AI systems are built using Machine Learning.
Which has a better salary—Data Science or AI?
Both fields offer high salaries. The salary depends more on your specific role, experience, and skills. Top-level AI Engineers and Data Scientists can earn very high salaries.
Can I learn ML without knowing Data Science?
You can, but it’s not a good idea. ML is all about learning from data. Data Science teaches you how to collect, clean, and prepare data. Without these basic data skills, building an effective ML model is very difficult.